Writing for the Web: A Beginner’s Guide
| 5 Min Read

Strong web writing skills are a key component of successful digital marketing strategy and effective search engine optimization (SEO). Though writing for the web encompasses a wide variety of different content, crafting the right kind of content is especially important for blog and website platforms. Writing for the web has its own set of best practices and style guidelines, especially because readers interact with web content differently than traditional text. For example, only around 16 percent of site visitors read web content in full. And according to the Nielsen Norman Group, about 80 percent of site visitors scan web content rather than reading it word by word.
How to Write for the Web
Add to these statistics the fact that most only scroll to the halfway point on a webpage, and brands have their work cut out for them in terms of connecting with the reader through content marketing. Why spend the time and resources to craft high-quality content if no one is reading it? This is the challenge facing marketers today. The good news is that there are ways to effectively reach modern readers — and hold their attention. It all starts with keeping copy concise, scannable and objective. The following are some of the key features of successful web writing.
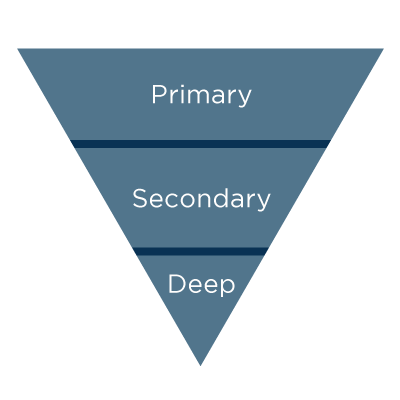
Inverted Pyramid Structure
Arguably the most important element of writing for the web is presenting information in a way that makes sense for the reader. Inverted pyramid structure, long used by journalists because it gets to the point quickly, puts the primary information first. Supporting information comes after, and the least important elements are at the end of the text. “Journalists have long adhered to the inverse approach: start the article by telling the reader the conclusion … readers can stop at any time and will still get the most important parts of the article,” the Nielsen Norman Group says. This means that writers should leave “deep content” for the relatively small number of readers who make it to the end of a piece, Moz says. This approach allows writers to prioritize information, and readers to choose how much detail they need on the topic: “Very interested readers will scroll, and these few motivated souls will reach the foundation of the pyramid and get the full story,” the Nielsen Norman Group explains.
Scannable Content
In addition to presenting the most important information first, web content should be easy to scan. Users rarely read to the end of content, so it is important to format text in a way that allows them to find the information they are looking for quickly and easily. Elements like headers, bold and highlighted text, bulleted lists, graphics, captions and more accomplish this. Enchanting Marketing offers the following (helpfully, bulleted) list of questions to evaluate whether your content is scannable to readers:
- Does your headline communicate what you’re about?
- Does your image caption communicate a message?
- Do your sub headlines summarize your key points?
- Do easy-to-scan bullet points reduce wordiness?
In general, “Your web visitor is hunting for information or products. Ensure he can understand your most important information by just glancing at your web page,” the same post says.
Concise Text
Because readers are looking to find information as quickly as possible, writing concise text is another key component of successful web writing. Users don’t stay on a page for very long. This is why marketers measure “bounce rate,” or the percentage of visitors who navigate away from content. To hold reader interest as well as maximize time on site, be as concise as possible. According to Buffer, the ideal length for a blog post is seven minutes, or 1,600 words. And for posts that incorporate many photos or other graphic elements, the average word count should be closer to 1,000. Though research varies from site to site, this gives content creators a good idea of what to aim for. Once again, Enchanting Marketing has provided a helpful checklist for keeping content short and sweet:
- Use short paragraphs
- Use short sentences
- Skip unnecessary words
- Avoid jargon
- Avoid the passive [voice]
- Avoid needless repetition
- Use the word “you”
Aside from actually writing less content, a good way to keep readers’ attention is to break up text into short paragraphs that can be easily scanned and digested. This works in tandem with concise text to ensure the user views as much content as possible.
Objective Language
Users want content to be easy to understand, and another way to accomplish this is by writing in a conversational, informal tone. Ensuring that your tone is objective makes information easier to process. Avoid overly promotional messaging because it makes users question the credibility of the content itself: “questioning the credibility of promotional statements seems to distract users from processing the meaning,” the Nielsen Norman Group says. This is also why Enchanting Marketing warns against using “clever phrasing.” Web writing should be as simple and easy to follow as possible. “Web visitors quickly glance at your web page before guessing whether they’re in the right place or not,” Enchanting Marketing says. “They just want to make a quick decision.”
Hypotext
One way to make your content more readable without sacrificing valuable information is to incorporate hypotext. According to Dejan Marketing, hypotext is “a way of revealing content on-demand. It acts like a traditional link, but it doesn’t interrupt user experience by sending readers to another page. Once clicked, the extra information is injected into a desired spot in the page. Another click hides it away.” By showing the most important parts of the content, readers can create their own experience. The same article provides several benefits of hypotext:
- Supports easy scanning and better content overview by removing visual clutter
- Encourages content consumption through low word count
- On-demand information retrieval enables interactivity and personalization
- Users stay on the page they’re reading, which minimizes interruption

From a content strategy perspective, hypotext also allows the writer to include more detailed information as an option while remaining concise.
As effective web writing becomes more and more important to overall marketing strategy, the volume of content being created is increasing at an unprecedented rate, according to Dejan Marketing. From blog posts to advertorials, opinion pieces and lists, the web is home to a wide variety of content competing for user attention. But if marketers can incorporate the best practices covered here, they stand to benefit from the world of opportunity that content marketing presents.
Creating optimized, high-quality content is one of the foundations of modern marketing strategy. If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to the marketing industry, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online marketing degree program.