Archive
Array

Did you know that 16 percent to 50 percent of the population consists of introverts? According to Psychology Today, these individuals gain energy from alone time rather than social interaction. They may get overwhelmed in large group situations and prefer to complete one task at a time, observing situations before getting involved. This is because “the brains of introverts and extroverts are wired differently,” Psychology Today explains.
The front of introverts’ brains are more active and stimulated by solitude, while the back portion of extroverts’ brains are more active. “This part of the brain is stimulated by sensory events coming in from the external world,” the same article notes. Because a chemical called dopamine is released in the brain when we experience pleasure, we are able to see that extroverts’ and introverts’ brains react differently. Extroverts need higher levels of dopamine, while introverts have a lower dopamine threshold.
These differences make the needs of introverts very different from those of extroverts. This is especially significant when it comes to career paths. Certain roles are ideal for introverts, while others are more suited to extroverted individuals.
Are You an Introvert?
These characteristics are typical for many introverts. You can use them as general guidelines when determining if you might be an introverted individual:
- Dislike small talk
- Prefer alternate forms of communication, such as emailing and instant messaging
- Require solitude to maintain energy levels
- Uncomfortable in networking situations
- Enhanced observational skills
- Sensitive to environmental stimuli, such as bright lights and loud noises
Top 8 Jobs for Introverts
The following careers are some of the best for introverts because they focus on working individually and require a detail-oriented approach.
Marketing
1. Social media manager
Social media managers are tasked with overseeing the entire social media presence of an organization. This includes managing multiple social media pages and communicating with both customers and vendors. Social media managers are responsible for implementing marketing campaigns that increase brand recognition and customer loyalty, PayScale explains. “They often serve as voices and liaisons for their organizations, as well as supervise and approve creative content and research new marketing techniques,” the same article continues. The median salary for social media mangers is $48,046.
2. Freelance content writer
Freelance writers work on a contract basis to produce editorial, advertising and other written content. They usually work from a home office or co-working space, which is ideal for introverts because they prefer to complete tasks alone. Freelance writers’ clients vary, but these professionals usually work closely with editors, designers and other creative roles. Prior writing experience is important for freelancers because they must seek out assignments on their own. The median hourly rate for freelance content writers is $24.71, according to PayScale.
3. Data analyst
Data analysts are responsible for conducting surveys and other methods for gathering information, then analyzing the data so it can be used by leaders and other stakeholders. They are responsible for compiling reports about their findings that can be easily understood by a variety of audiences. It is important for data analysts to be experienced in computer programs like Microsoft Excel, Sharepoint and SQL databases, PayScale notes. Other job responsibilities include identifying new sources of data, staying up to date with the latest data collection methods and more. The median salary for data analysts is $57,551.
Health Care
4. Medical transcriptionist
Medical transcriptionists are tasked with transferring codes from doctors’ notes and adding them to digital databases. Because this role is so detail-oriented, it is critical for medical transcriptionists to be aware of the latest changes to medical and diagnostic codes. “Much of the work is done independently, so it is important to be self-motivated and to be able to adhere to guidelines. Attention to detail is also an essential personality aspect, as accuracy is needed,” PayScale explains. The median hourly rate for medical transcriptionists is $15.28.
5. Private duty nurse
Private duty nurses are responsible for providing medical care to patients in their homes. They have a variety of job duties, including assisting with movement, preparing meals, monitoring vital signs and managing medications. Private duty nurses also ensure patients are safe and as comfortable as possible while assisting with daily activities. The median hourly rate for private duty nurses is $23.85.
Finance
6. Accountant
Certified public accountants (CPAs) “handle the accounting, tax, reporting and/or audit processes for governments, corporations or individual clients,” according to PayScale. Depending on specific client needs and area of specialization, they may also review financial information, prepare documentation, complete tax forms and more. It is particularly important that accountants are aware of new government regulations. CPAs also ensure compliance with laws while maintaining detailed records of all assets, profits and losses. The median annual salary for this role is $63,214.
7. Financial advisor
Financial advisors usually work for banks, mutual fund companies and insurance companies. They work with clients on an individual basis to “assess their financial needs and help them achieve financial goals … and they also explain tax laws relevant to certain investments and help with insurance decisions,” according to PayScale. Financial advisors also help their clients plan for life events such as retirement and children attending college. They recommend smart investments while managing risk. The median salary for financial advisors is $58,539.
8. Auditor
Auditors are responsible for ensuring the accuracy of financial records. They “form opinions based on sufficient, competent material that is relevant to the auditor’s aim,” PayScale explains. Auditors can either be self-employed or work internally at a private organization or for the government. They are responsible for sharing their findings with others, including executives and stakeholders. The median annual salary for auditors is $54,223.
Note: All salary information reflects available data at time of publication.
If you are interested in topics like this one, Concordia University, St. Paul’s online programs may be right for you. With degrees in high-demand fields like health care, marketing, business and more, Concordia offers flexible options that allow you to study when and where you can while balancing other responsibilities. You can become a successful professional with the right degree. Let Concordia get you there. Many of Concordia’s undergraduate and graduate programs are available both online and on campus.
Array

While there are standard elements that should be included on any resume regardless of industry, those in creative fields need to cater their resumes to provide employers with an understanding of their skill level and ability. Many creative positions require resumes that include elements beyond the standard work history and education. Professionals in creative industries can stand out by catering their resumes to showcase their creative achievements.
Most recruiters spend an average of six seconds scanning resumes before choosing candidates to interview, according to Career Cloud. This makes standing out critical — you have a very short time to catch the hiring manager’s eye. When putting together your creative resume, it’s important to keep in mind that you’re presenting a “written picture that lays out your career, skill, ambitions, and drive. When done correctly, it should have some (but not all) of your personality, and should showcase your skills in the best way possible,” Career Cloud explains. Above all, your resume should represent who you are as a professional and what you bring to the table.
Creative Resume Do’s and Don’ts
There are many best practices to incorporate as you craft your creative resume. First, be sure to showcase your skills. Your resume should focus on what you can do and how potential employers stand to benefit from bringing you onboard. To accomplish this, include specific examples of industry skill sets you have. You should also include relevant keywords that make sense for the role you’re seeking. Because many companies now use software to scan resumes for promising candidates, you’ll need to incorporate keywords to make it past the first round in many cases.
Another best practice for creative resumes is quantifying your accomplishments. Just because you work in a creative field doesn’t mean employers don’t want proof you can execute. “Don’t just say what you have done, put direct facts, numbers, and data behind it. You can use range, project scope, audience, impact, scale, or frequency in your numbers,” Career Cloud notes. In addition, use your creativity to ensure that your resume tells a story — don’t just list facts. Move from one section to the other logically so that employers can learn more about you.
There are also certain things to steer away from when putting together a creative resume. First, while it’s important to include relevant keywords, don’t copy the job posting word-for-word. Recruiters want to know what unique qualifications you have that make you a great fit for the role. Also, don’t overshare personal information about yourself. Creative resumes have to walk a fine line between being creative and being informative, so remember to keep it professional.
Also, don’t include every detail of your work history. Common practice is one page per 10 years of work experience, because hiring managers won’t keep reading if your resume is too lengthy. Include only the most relevant and impressive information you have to offer. Finally, don’t use too many different fonts and colors. Unless you’re applying for a graphic design role (which we discuss below), your creativity should come from the words you choose and how you present information rather than using several different visual elements. This ensures your resume is cohesive, readable and dynamic.
Customize Your Creative Resume
Because creative professions are highly specialized, there is no one-size-fits-all approach to putting together a great resume. The following are some of the key ways you can tailor your creative resume to a specific role.
Graphic Designers
Graphic designers should treat their resume as a portfolio sample, according to Company Folders. It is especially important for graphic designers to create a resume that echoes their style and creativity. Especially for this type of creative role, many of the traditional rules of resume creation don’t apply. For example, using a variety of (cohesive) colors and fonts can make graphic design resumes stand out.
Graphic designers should also use design software like InDesign or Adobe Illustrator when designing their resume. Finally, it’s a good idea for graphic designers to have a consistent brand across their resume, portfolio, website and other professional assets.
Writers
For writing roles such as those in communications or copywriting, focusing on your relevant experience is most important. Even if your previous work experience has been freelance, create entries on your resume that describe the work you did. In addition, writers should include a list of published work. “Separate your publications into different categories based on genre (e.g., short stories, fiction, books, e-books, newsletters, magazine articles, newspaper articles, Web site copy, blogs, etc.),” Monster notes.
Because you’ll likely be asked for work samples, you should also put together a portfolio of your best examples. ”You can have them nicely bound in a portfolio for your hard-copy presentation,” Monster says, but it’s a good idea to have links ready to email or even a website that showcases your work.
Marketers
Resumes for marketing professionals are perhaps the most traditional of all creative resumes. Because marketing is still largely a business-based role, professionals should incorporate most of the elements of a standard resume. In addition, marketers should draw on their existing skill sets to understand their target audience. “If you know who will read it and what’s important to them, you can shape your message accordingly. To do this, you need to think about the type of job and company you’re hoping to work for,” HubSpot explains.
You should also include specific metrics to help hiring managers understand your goals. These might include improving social media engagement, boosting web traffic and conversions, reducing bounce rates and more. Consider highlighting quantified campaign results as the focus of your resume.
If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to creative professionals, Concordia University, St. Paul offers a variety of fully online programs designed to help you become a successful professional in your chosen field. The online Bachelor of Science in Marketing program combines foundational skills in marketing with practical business knowledge.
For those interested in creative writing careers, Concordia also offers an online Master of Fine Arts in Creative Writing that combines theoretical inquiry with practical application, preparing students to become professional writers. Many of Concordia’s programs are available both online and on campus.
Array

Many business professionals will experience a merger during the course of their careers. In fact, mergers and acquisitions are common business practices, particularly in industries like health care, technology, finance and retail. With the rapid pace of innovation in the modern business world, it’s important to understand why — and how — mergers and acquisitions happen.
Why Companies Merge
In many cases, synergy is the cause. This term refers to the practice of combining business activities to increase performance while decreasing costs. When two businesses have complementary strengths and weaknesses, Investopedia notes that merging makes strategic sense.
In other cases, mergers occur as a means of diversifying or sharpening the focus of a business. “A company that merges to diversify may acquire another company in a seemingly unrelated industry in order to reduce the impact of a particular industry’s performance on its profitability. Companies seeking to sharpen focus often merge with companies that have deeper market penetration in a key area of operations,” Investopedia explains.
Mergers can also help companies grow market share by purchasing a competitor’s business. This practice is referred to as a horizontal merger, while vertical mergers are focused on the supply chain. “If a company buys out one of its suppliers, it is able to save on the margins that the supplier was previously adding to its costs,” according to Investopedia. Especially in the case of buying out a distributor, this type of merger can have a significant positive impact on production costs.
Of course, one of the most common reasons for pursuing a merger is eliminating competition from other businesses. When a company acquires a competitor through an acquisition deal, it can gain a much larger market share in one fell swoop. However, this practice can be costly, so it is important for businesses to be sure of the benefits before choosing to begin a merger and acquisition deal. Investopedia notes that “a large premium is usually required to convince the target company’s shareholders to accept the offer” rather than sell their shares.
Top Mergers
The following are among the biggest mergers of all time.
Vodafone and Mannesmann
This merger, which took place in 2000, was worth over $180 billion and is the largest merger and acquisition deal in history. In it, U.K.-based Vodafone acquired German company Mannesmann. As a result, Vodafone became the largest mobile operator in the world while setting the stage for future deals in the telecom industry. Many Germans were against this deal because they wanted German businesses to remain key players in the global marketplace.
The deal was significant because it signaled the telecom boom as mobile phones began increasing in popularity. However, it was not ultimately successful. “After Mannesmann rejected Vodafone’s first offer, Vodafone had to nearly double its offer…Unfortunately, the combination didn’t work out the way Vodafone hoped, and as a result, it had to write off tens of billions of dollars in the following years because of it,” Business Insider explains.
America Online and Time Warner
This merger is the second largest in history, and it took place during the same year as the Mannesmann acquisition. In 2000, America Online (more widely known as AOL) acquired Time Warner for $164 billion. At the time, most Americans used their landline phone service to access the internet through provider AOL, making the company one of the biggest technology organizations in America. Though expensive, this deal lasted only nine years. In 2009, Time Warner became an independent company as AOL continued to lose value in the post-dial-up age.
Pfizer and Warner-Lambert
Also in 2000, pharmaceutical company Pfizer acquired Warner-Lambert for $90 billion. This merger is considered by some experts to be “one of the most hostile in history” because Warner-Lambert was originally to be purchased by consumer goods company American Home Products. However, American Home Products “walked away from the deal with $1.8 billion worth of break-up fees, one of the largest ever payouts for a failed deal,” according to Yahoo Finance.
When Pfizer acquired Warner-Lambert, the result was the second largest drug company in the world. The main reason for the acquisition was ownership of top-selling cholesterol medication Lipitor: “Pfizer had commercial rights to Lipitor, but Pfizer was splitting profits on it with Warner-Lambert, and in 1999, Warner-Lambert sued Pfizer to end their licensing pact,” Business Insider explains. By acquiring Warner-Lambert, Pfizer removed any risk associated with the lawsuit and gained sole control of Lipitor’s skyrocketing profits, which grew to more than $13 billion annually.
AT&T and BellSouth
In 2006, AT&T announced its plans to acquire BellSouth. This deal would ultimately cement AT&T’s place as a major player in the wireless industry. In purchasing BellSouth for $86 billion, AT&T was able to expand coverage into rural areas of the United States, giving AT&T an advantage as the mobile phone market expanded. “The firm used its new position to create bundled services that included mobile services along with television and internet connections in an effort to gain new subscribers and dissuade customers from switching to new providers,” Yahoo Finance explains.
Exxon and Mobil
This merger took place in 1999 and created a “superpower” in the energy industry. Oil prices were consistently low, and energy companies were taking a hit as a result. This led Exxon and Mobil to merge in a deal that Yahoo Finance calls “one of the most successful in M&A history.” The U.S. government approved the deal after assurances that the two merging companies would sell over 2,400 gas stations across the country. “Exxon defended the deal, the largest in a string of consolidation moves in the industry, citing price pressure on crude oil, the need for greater efficiency and new competitive threats overseas,” CNN Money explains.
Online Programs from CSP Global
If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to the business world, consider CSP Global’s online Bachelor of Arts in Business degree, which provides students with a strong foundation of business skills. For professionals ready for advanced business education, CSP Global offers a fully online MBA. Through mentorship and advanced coursework in core business topics, this program provides students with skills to advance their careers while becoming experts in their chosen industry. Many of CSP Global’s programs are available both online and on campus.
Array

With department store giants such as Sears and J.C. Penney closing flagship stores at a rapid pace, the retail sales decline has been making headlines, especially over the last two years. Due to years of building new retail spaces only to be eclipsed by the rise of online shopping, traditional retail is in trouble. According to eMarketer, U.S. department stores sales “have been on a steady decline over the past decade, shrinking from $87.46 billion in 2005 to $60.65 billion in 2015.”
And this trend is expected to continue. As Mark Cohen, director of retail studies at Columbia Business School, told The Wall Street Journal, “There is no reason to believe that this will abate at any point in the foreseeable future.” In fact, as of April 6, the same article notes that retail store closings are expected for 2,880 locations, including large national brands such as Payless ShoeSource. “That is more than twice as many closings as announced during the same period last year,” the article continues, citing Credit Suisse. This means that there will be more retail stores closing in 2017 than during the 2008 recession.
When it comes to brick-and-mortar stores, consumers are more interested in fast-fashion and discount chains, making it difficult for other retailers to stay competitive in terms of price. As more companies turn to e-commerce in order to boost sales, they can expect smaller profits. Because of shipping and technology costs, online retail is more expensive for businesses. Retailers don’t have much of a choice, however, according to the WSJ: “Retail margins on average fell to 9% last year from 10.5% in 2012, according to consulting firm AlixPartners LP. Over that period, e-commerce sales increased to 15.5% of total sales.” For most companies, that means accepting smaller profits and shifting focus toward online sales.
Major Reasons for the Retail Sales Decline
Several factors combined have caused retail sales to decline in the past few years. The first is that consumers have become more aware of their own agency and options. Customers take a new approach to making purchases, one that emphasizes price comparison and the ability to purchase through different platforms. They might combine online shopping with a visit to a specific retailer or third-party seller in the same trip in order to find the best deal.
Perhaps most obviously, an increase in online shopping has directly led to a decline in retail sales. In fact, Amazon alone accounted for 53 percent of all U.S. e-commerce growth in 2016. Of course, most retailers offer online shopping in addition to brick-and-mortar locations, but the overall rise of online shopping has been detrimental to in-store sales. Many customers choose to shop online because of convenience, and that’s something retailers just can’t compete with.
To stay competitive, companies also have to offer steep discounts and near constant promotions, and their brands have suffered as a result. Deep discounts devalue the brand because it’s no longer aspirational to consumers. In addition, once retailers begin offering frequent sales, customers come to expect a discount rather than paying full price. Finally, as millennials make up more and more of the buying public, retailers have to adapt to a new type of customer. Millennials want to feel entertained and engaged when they shop, so retailers are faced with overhauling their layout and buyer approaches to create a more boutique experience.
Results of Decline
As a result of the overall decline in retail sales, both shopping malls and department stores are experiencing high rates of closure. According to Business Insider, around 15 percent of U.S. malls will either fail or convert to non-retail space by 2024. Together, J.C. Penney, Macy’s and Sears have closed hundreds of stores since 2010 and laid off employees; Sears even closed its flagship store in Chicago, the same article explains. As these once-ubiquitous department stores close more doors, malls are choosing to replace them with movie theaters and restaurants rather than more retail spaces.
Department stores are often referred to as “anchors” because, at one time, they were the main reason consumers came to shopping malls. With that no longer being the case, malls are decreasing the number of anchors they need to stay afloat. “You’re seeing centers that used to have four anchoring department stores get away with just one,” an expert told TIME Money. In addition, many department store brands are shuttering altogether. Less than two decades ago, there were about 20 department store brands in American malls. Today, TIME Money reports, there are only eight.
Shoppers just aren’t as interested in the all-purpose shopping experience as they used to be. “For the most part, department stores have been painted as boring, overpriced, middle-of-the-road, and inconvenient compared to the other options out there … Nowadays, having Macy’s or Sears as an anchor is arguably a bad thing; it’s keeping the mall stuck in the past, preventing it from being where shoppers want to go,” TIME Money says.
Future Predictions for Retail
While the situation appears stark, there is a future for retail if companies are willing to adapt. It’s time to modernize in order to compete with the convenience of online shopping and changing consumer tastes. The “stores of the future” will need to create engaging shopping experiences that make coming to a brick-and-mortar store worthwhile. Forbes recommends incorporating elements like “active participation, the co-creation that makes memories, and loyal customers.”
One of the ways to achieve this is through omnichannel retailing. This strategy means that retailers “will be able to interact with customers through countless channels—websites, physical stores, kiosks, direct mail and catalogs, call centers, social media, mobile devices, gaming consoles, televisions, networked appliances, home services, and more,” according to the Harvard Business Review.
If incorporating all those channels into a cohesive strategy sounds daunting, think of it in terms of what customers want. Omnichannel retailing combines the benefits of shopping online, such as a wide selection and customer reviews, with the advantages retailers bring to the table, like personal service. It’s all about reaching consumers wherever they are. Because different types of customers value different things, integration is the smartest way for retailers to innovate and bring shopping into the modern era.
If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to entrepreneurs and other business professionals, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s MBA program. Through mentorship and advanced coursework in core business topics, this program provides students with skills to advance their careers while becoming experts in their chosen industry. This program is available both online and on campus.
Array

Drop shipping is a retail business model; however, it differs from traditional models in that the owner only purchases product from a vendor when an order has been placed by a customer. This eliminates the need to own or store inventory and opens up a wide range of opportunities for entrepreneurs. Drop shipping refers to a process in which products ship directly from supplier to customer, rather than shipping to the business itself first, thus streamlining the process.
The core benefit of drop shipping is that it saves on resources and time. When you don’t have to pack and ship your own products, you can devote resources to other core business processes. Working with drop shipping partners “is not only a product acquisition model, but also includes product fulfillment,” according to Shopify.
How Does Drop Shipping Work?
The drop shipping model is relatively simple. It consists of the following steps:
- A customer places an order with an online business.
- The business receives the order and forwards it to the drop shipping partner.
- The drop shipper packs and sends the products in the order directly to the customer on behalf of the business.
- The customer receives the products ordered.
Pros and Cons of Drop Shipping
Aside from the central benefit of eliminating costs associated with storing, packing and shipping products, here are some of the key benefits of drop shipping:
Lower capital requirement: Due to the nature of the business model, utilizing drop shipping helps cut typical business spending. It’s a cheap way to start a business because it keeps startup costs low. It also does away with inventory management practices, typically one of the most prohibitive costs for new businesses.
Wider product selection: Because it gives you access to new products, niche items and best-sellers, Volusion says that drop shipping “can effectively increase the variety of products your online business sells.” E-commerce incubator A Better Lemonade Stand also points out that it’s easy to diversify inventory by merely adding new items to your store.
Reduced risk: Without drop shipping, businesses take on a great deal of risk when purchasing inventory due to the potential for excess inventory or under-ordering, Volusion notes. Drop shipping frees you from purchasing items you may not be able to sell.
Flexibility: Dropping shipping allows you complete location independence. This means that you can operate anywhere that has an internet connection instead of worrying about storage space.
Scalability: You can easily scale your business up and down because you don’t have to manually fulfill each order. Selling 10 or 10,000 units requires roughly the same amount of work.
There are also complexities and potential drawbacks associated with drop shipping. Here are some of the disadvantages to the model:
High competition: More people tend to choose drop shipping because of the benefits listed above. This increases competition, meaning that businesses should have a selling point that differentiates them from the competition.
Low margins: Slim margins mean that businesses have to be able to move a lot of product in order to make enough profit. In addition, it can be difficult to execute paid marketing campaigns to attract new customers.
Limited brand control: Because it utilizes third-party shippers, drop shipping limits businesses’ ability to control branding and customer experience.
Despite these disadvantages, drop shipping is the right choice for many entrepreneurs. For example, entrepreneurs who are looking to test new products before investing a large amount of time and money into them will benefit from the flexibility of the drop shipping model. Entrepreneurs who are just starting out in e-commerce may find drop shipping to be a great business model because it is relatively low-touch and gives them a chance to gain valuable experience, A Better Lemonade Stand notes. However, it is important to note that, as is the case with all business decisions, you should think critically and understand your specific requirements before choosing drop shipping to build a successful online business.
If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to entrepreneurs and other business professionals, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online MBA program. Through mentorship and advanced coursework in core business topics, this program provides students with skills to advance their careers while becoming experts in their chosen industry. An online MBA in Health Care Management is also available.
Array

One of the latest emerging technologies in the manufacturing industry is 3D printing. In fact, the 3D printing industry grew by more than 35 percent in 2014 alone, according to Harvard Business Review (HBR). But what is this emerging technology? And how does it work?
What Is 3D Printing?
Also known as additive manufacturing, rapid prototyping or solid free-forming technology, the process creates 3D objects by building multiple layers of material. Working from a computer model, it allows manufacturers to “devise completely new shapes without regard for existing manufacturing limitations,” according to MIT Technology Review. The process uses Computer Aided Design (CAD) software by reading data from the CAD file and adding successive layers of liquid, powder or sheet material in a layer-upon-layer fashion to create a 3D object.
While traditional manufacturing methods rely on the removal of excess materials, 3D printing is additive, meaning it only uses the materials required to create the product. This increases precision while removing waste and extraction costs, HBR explains. Though there are many exciting opportunities for utilizing additive manufacturing, “the most transformative applications for this technology will need time to evolve,” according to “Medical Applications for 3D Printing: Current and Projected Uses” by C. Lee Ventola.
3D printing is expected to transform the medical field, with experts comparing it to the impact of the printing press.
Applications of this relatively new technology can be seen in enterprises ranging from engineering to textiles, but perhaps one of the most exciting uses of 3D printing is in the health care field. In fact, 3D printing is expected to transform the medical field, with experts comparing it to the impact of the printing press. There are many uses for 3D printing in health care, including tissue fabrication, anatomical models and pharmaceutical research, Ventola says.
3D Printing in Medicine
As leading researchers become more familiar with the capabilities of 3D printing, they are finding many ways to incorporate the technology. For example, HBR notes that it has been used to create 3D-printed skin for burn victims and airway splints for babies with tracheobronchomalacia, a disease of the central airways. What’s most notable about the latter application is that the splints can be created quickly, cost about $10 per unit and are designed to grow with the patient, the same article notes.
Scientists at Princeton University have also discovered that 3D printing technology can be used to “create a bionic ear that can hear radio frequencies far beyond the range of normal human capability, in a project to explore the feasibility of combining electronics with tissue,” HBR reports. And because these exterior uses are going well, there is a real possibility that 3D printing will be used to replicate internal organs in the future, mitigating the need for donor waiting lists.
3D printing is an exciting prospect for cancer treatment as well. Researchers created facial prostheses for eye cancer patients in 2014, and another research team was able to print “patient-specific, biodegradable implants to more effectively cure bone infections and bone cancer,” according to HBR. Like most additive manufacturing applications, these technologies are inexpensive and efficient to use.
Scientists are finding other ways to apply additive manufacturing technology, and its use goes beyond life-threatening medical conditions into more conventional medical practice. For example, 3D-printed casts and pharmaceuticals have been developed in recent years. “The 3D-printed cast, for example, heals bones 40-80% faster than traditional casts. 3D-printed pills allow for interesting new pill shapes that completely alter the drugs’ release rates,” HBR reports. It is important to note that these technologies are in the early or research stages and aren’t yet available for widespread use.
What the Evolving 3D Printing Process Means for Medicine
There are many advantages to incorporating additive manufacturing into the health care industry. Perhaps the most critical is the ability to create custom products and equipment. Personalized implants and tools can decrease the time needed to perform surgery as well as speed up patient recovery time, Ventola says. In addition, customization can improve the changes of a treatment or procedure’s success. “It is also anticipated that 3D printing technologies will eventually allow drug dosage forms, release profiles, and dispensing to be customized for each patient,” the same article continues.
The advent of 3D printing stands to decrease health care costs. Medical items can be produced quickly and cheaply, especially for small prosthetics and implants. This is especially relevant for spinal, dental and craniofacial disorders, Ventola explains. Even printing custom products is relatively inexpensive. Savings during the manufacturing phase can be passed on to patients as well, lowering health care costs across the board.
Finally, 3D printing is creating a climate of collaboration as materials become more widely available and costs decrease. “This allows more people, including those in medical fields, to use little more than a 3D printer and their imaginations to design and produce novel products for personal or commercial use,” Ventola says. Now more than ever, researchers can test promising ideas and share their work with others. Using downloadable open-source files, work can be replicated exactly. This has democratized the research and development process.
The Future of Medical 3D Printing
It is clear that innovation in additive manufacturing presents a host of benefits that could revolutionize the health care industry. New developments like the ones featured here have “the potential to disrupt the alarming trajectory of rising health care costs at exactly the moment when aging Baby Boomers will be putting more pressure on the health care system,” HBR says. This makes 3D printing a vital topic for health care professionals in a wide variety of roles.
If you are interested in health care topics like these, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online MBA program in Health Care Management. With coursework that focuses on both core business topics and the latest trends in the health care industry, this degree prepares graduates with the confidence to succeed in their chosen career path.
Array

When it comes to careers in the business world, much emphasis is placed on mastering hard skills. However, developing soft skills is also a key component of success. During the hiring process, employers and human resources teams look for applicants who balance both hard and soft skills because these well-rounded candidates are valuable in a variety of positions. But what are hard and soft skills, and what impact do they have in the workplace?
Hard skills are “teachable abilities or skill sets that are easy to quantify,” according to The Balance. These skill sets are often featured on cover letters and resumes so that they are easily recognizable to recruiters. Soft skills, on the other hand, are more subjective. Also known as “people skills,” they refer to how an individual interacts with others, The Balance explains.
Hard Skills vs. Soft Skills
While hard skills can be taught through training and professional development, it’s much more difficult to teach someone soft skills. Think of it this way: A candidate can easily use tutorials to learn a computer program that is new to them, but developing skills like teamwork and time management is a more complex process. That’s why more and more employers are seeking out candidates with a combination of both skill sets. If a professional can already demonstrate valuable soft skills, employers can make use of their potential for ongoing success.
There are a few key differences between hard and soft skills. The first is related to types of intelligence. In general, soft skills require emotional intelligence (EQ), while hard skills are more based in assessments such as the intelligence quotient (IQ).
EQ is “the ability to identify, assess, and control the emotions of oneself, of others, and of groups,” according to Diffen. Examples of EQ include collaboration and initiative. Conversely, IQ is derived from standardized testing and grades. It usually refers to the ability to “learn, understand and apply information to skills, logical reasoning, word comprehension, math skills, abstract and spatial thinking” and more, Diffen continues. Hard skills are important when it comes to analysis, research and development.
Another difference between hard and soft skills is in how each skill set is developed. Hard skills are typically learned via coursework or training, while soft skills tend to be more innate or developed indirectly through experience. Finally, hard skills vary by industry and profession: An accountant relies on different soft skills than a marketing manager would, for example. Soft skills are more general and can be utilized across many fields.
Hard Skills
- Project management: Project management skills enable business professionals to manage a team and execute projects effectively. Being able to navigate complex projects is a cornerstone of leadership and can make the difference between failure and success.
- Technology management: Because technology is such a driving force in the business world, navigating the various tech components of a business is an invaluable hard skill. Understanding the connection between business and technology is one of the best ways to advance in your career.
- Information analytics: Information analytics can increase productivity and drive businesses, helping them to stay competitive. Utilizing this skill set helps businesses understand consumer behavior.
Soft Skills
- Interpersonal communication: According to a GMAT survey of employers, communication skills are among the most in-demand for new hires. “Communications, teamwork, and interpersonal skills are critical—everything we do involves working with other people,” one employer said.
- Leadership: Successful managers and others in advanced positions need to be able to lead their employees while motivating them to perform at a high level. “A good leader will inspire those who work with them and around them, make them feel valued and give the whole undertaking a sense of direction,” Top MBA says.
- Decision-making: Being able to think strategically and make tough decisions is one of the core skills business leaders need.
Skill Development Through MBA Coursework
Both hard and soft skills can help professionals stand out from the competition and gain ongoing career success. Earning a Master of Business Administration (MBA) is a smart way to hone both skill sets. Concordia University, St. Paul’s fully online MBA balances coursework in core business topic areas like finance and accounting with hands-on projects and research that help students develop strong soft skills.
If you are interested in advanced business topics like these, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online MBA program. You can also download our free guide, “Climbing the Corporate Ladder: Your Guide to the MBA and Beyond,” for an in-depth look at the value of the MBA.
Array

In general, the decision making process helps managers and other business professionals solve problems by examining choices and deciding on the best route to take. Using a step-by-step approach is an efficient way to make thoughtful, informed decisions that positively impact your organization’s short- and long-term goals.
The business decision making process is commonly divided into seven steps. Managers may utilize many of these steps without realizing it, but gaining a clearer understanding of best practices can improve the effectiveness of your decisions.
Steps of the Decision Making Process
The following are the seven key steps of the decision making process.
1. Identify the decision
The first step in making the right decision is recognizing the problem or opportunity and deciding to address it. Determine why this decision will benefit your customers or fellow employees.
2. Gather information
Next, it’s time to gather information so that you can make a decision based on facts and data. This requires making a value judgment, determining what information is relevant to the decision, and how you can get it. Ask yourself what you need to know to make the right decision, then actively seek out anyone who needs to be involved.
“Managers seek out a range of information to clarify their options once they have identified an issue that requires a decision. Managers may seek to determine potential causes of a problem, the people and processes involved in the issue, and any constraints placed on the decision-making process,” according to Chron Small Business.
3. Identify alternatives
Once you have a clear understanding of the issue, it’s time to identify the various solutions at your disposal. You likely have many options when deciding, so it is essential to come up with a range of options. This helps you determine which course of action is the best way to achieve your objective.
4. Weigh the evidence
In this step, according to management experts Phil Higson and Anthony Sturgess, you’ll need to “evaluate for feasibility, acceptability and desirability” to know which alternative is best. Managers need to be able to weigh the pros and cons, then select the option that has the highest chance of success. It may be helpful to seek a trusted second opinion to gain a new perspective on the issue.
5. Choose among alternatives
When it’s time to make your decision, be sure you understand the risks involved with your chosen route. You may also select a combination of alternatives now that you fully grasp all relevant information and potential risks.
6. Take action
Next, you’ll need to create an implementation plan. This involves identifying what resources are required and gaining support from employees and stakeholders. Getting others on board with your decision is a key component of executing your plan effectively, so be prepared to address any questions or concerns.
7. Review your decision
An often-overlooked but important step in the decision making process is evaluating your decision for effectiveness. Ask yourself what you did well and what can be improved next time.
If your decision didn’t work out the way you planned, you may want to revisit some of the previous steps to identify a better choice.
Common Challenges of Decision Making
Although following the steps outlined above will help you make more effective decisions, there are some pitfalls to look out for. Here are common challenges you may face and best practices to help you avoid them.
- Having too much or not enough information. Gathering relevant information is key when approaching the decision making process, but it’s important to identify how much background information is truly required. “An overload of information can leave you confused and misguided, and prevents you from following your intuition,” according to Corporate Wellness Magazine.
In addition, relying on one single source of information can lead to bias and misinformation, which can have disastrous effects down the line.
- Misidentifying the problem. In many cases, the issues surrounding your decision will be obvious. However, there will be times when the decision is complex and you aren’t sure where the main issue lies. Conduct thorough research and speak with internal experts who experience the problem firsthand to mitigate this. Corporate Wellness Magazine says it will save you time and resources in the long run.
- Overconfidence in the outcome. Even if you follow the steps of the decision making process, there is still a chance that the outcome won’t be exactly what you had in mind. That’s why it’s so important to identify a valid option that is plausible and achievable. Being overconfident in an unlikely outcome can lead to adverse results.
Decision making is a vital skill in the business workplace, particularly for managers and those in leadership positions. Following a logical procedure like the one outlined here and being aware of common challenges can help ensure both thoughtful decision making and positive results.
If you are interested in business management topics like these, consider CSP Global’s online MBA program. You can also download our free guide, “Climbing the Corporate Ladder: Your Guide to the MBA and Beyond,” for an in-depth look at the value of the MBA.
Array

Interpersonal communication is a soft skill that encompasses how well an individual communicates with others. This skill set, also referred to as “people skills” or “social skills,” is one of the most important for success in the workplace. Communication can take place both verbally and nonverbally, either in person or through digital means such as email or instant messaging. In communication theory, there are six key components of interpersonal communication:
- The communicators: This refers to both the sender of the communication and the receiver. There are at least two communicators involved in all interpersonal communication.
- The message: One of the most important parts of interpersonal communication is the message. It can be conveyed in many ways: speech, body language, tone of voice, gestures and other indicators. Non-verbal messages provide additional information that may not be readily apparent through words.
- Noise: This refers to any distortion that causes differences between what is received and what it sent, according to resource website CommunicationTheory.org. Examples of noise include jargon, language barriers, inattention and more.
- Feedback: Feedback is the response of the receiver. In other words, it’s the message sent back to the sender. This allows the sender to know whether the message has been received and interpreted correctly.
- Context: Whether a message is received and interpreted correctly depends largely on context. “The emotional climate and expectations of the people, the place of occurrence, and social, political, cultural and environmental conditions comprise context,” CommunicationTheory.org says.
- Channel: Finally, this component refers to how the communication occurs. A message is sent and received through a specific channel, or medium.
Interpersonal Communication in the Workplace
Interpersonal communication is one of the most important life skills business professionals can have. In companies and organizations of all types, effective communication determines whether a team can operate effectively and accomplish core business goals. “It underlies the efficiency of key business functions such as managing, training, selling and resolving conflicts within an organization,” Chron Small Business explains.
Elements of Interpersonal Communication
Interpersonal communication can also be divided into subskills. Effective communication in the workplace relies on each of the following elements:
- Problem solving and decision making: One of the best ways to maintain professional relationships is through effective problem solving and decision making. Both of these skills align team members toward a common goal. If leaders are unable to take the steps necessary to solve problems and make the right decision for the team, a business can’t function successfully.
- Listening: Strong listening skills are invaluable for business professionals. They help individuals understand sent messages and act accordingly. If a manager provides instructions but team members are unable to listen and synthesize the information, roadblocks will arise that can derail projects and cause negative consequences.
- Assertiveness: A commonly undervalued element of interpersonal communication is assertiveness. The ability to influence others helps leaders drive the team toward a common goal. Being willing to take charge and effect change is one of the hallmarks of a business leader.
- Negotiation: This skill is a key element in conflict resolution. Finding common ground and identifying shared goals can help business professionals work effectively with others.
How to Improve Interpersonal Communication in the Workplace
Here are some of the ways business professionals can improve interpersonal communication in the workplace.
- Research and plan: Gather facts and relevant data to plan for important conversations. This helps ensure clarity and accuracy.
- Determine your audience: Consider coworkers’ personality and mindset before approaching a conversation. Find the right communication style for your specific situation. Some conversations lend themselves to face-to-face meetings, while others can be best accomplished through email.
- Self-evaluation: Understand your own strengths and weaknesses when it comes to communication. Ask for honest feedback from coworkers and managers as a learning opportunity to better inform future interactions.
- Monitor expectations: Keep assumptions and expectations to a minimum before engaging with a coworker. You never know for sure how someone will react, so be ready to adapt as the situation demands.
Skill Development Through Graduate Coursework
Earning a Master of Business Administration (MBA) is an ideal way to develop stronger interpersonal communication skills. Concordia University, St. Paul’s fully online MBA balances advanced business coursework with hands-on projects that help students develop real-world skills for the workplace. On campus program options are also available.
If you are interested in advanced business topics like these, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online MBA program. You can also download our free guide, “Climbing the Corporate Ladder: Your Guide to the MBA and Beyond,” for an in-depth look at the value of the MBA.
Array

Strong web writing skills are a key component of successful digital marketing strategy and effective search engine optimization (SEO). Though writing for the web encompasses a wide variety of different content, crafting the right kind of content is especially important for blog and website platforms. Writing for the web has its own set of best practices and style guidelines, especially because readers interact with web content differently than traditional text. For example, only around 16 percent of site visitors read web content in full. And according to the Nielsen Norman Group, about 80 percent of site visitors scan web content rather than reading it word by word.
How to Write for the Web
Add to these statistics the fact that most only scroll to the halfway point on a webpage, and brands have their work cut out for them in terms of connecting with the reader through content marketing. Why spend the time and resources to craft high-quality content if no one is reading it? This is the challenge facing marketers today. The good news is that there are ways to effectively reach modern readers — and hold their attention. It all starts with keeping copy concise, scannable and objective. The following are some of the key features of successful web writing.
Inverted Pyramid Structure
Arguably the most important element of writing for the web is presenting information in a way that makes sense for the reader. Inverted pyramid structure, long used by journalists because it gets to the point quickly, puts the primary information first. Supporting information comes after, and the least important elements are at the end of the text. “Journalists have long adhered to the inverse approach: start the article by telling the reader the conclusion … readers can stop at any time and will still get the most important parts of the article,” the Nielsen Norman Group says. This means that writers should leave “deep content” for the relatively small number of readers who make it to the end of a piece, Moz says. This approach allows writers to prioritize information, and readers to choose how much detail they need on the topic: “Very interested readers will scroll, and these few motivated souls will reach the foundation of the pyramid and get the full story,” the Nielsen Norman Group explains.
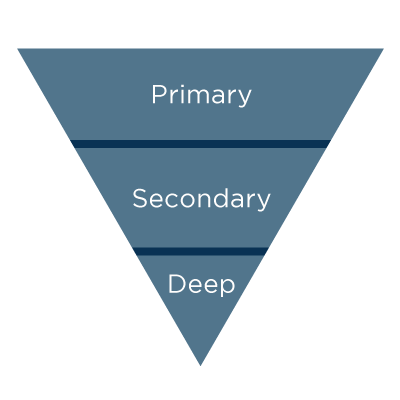
Scannable Content
In addition to presenting the most important information first, web content should be easy to scan. Users rarely read to the end of content, so it is important to format text in a way that allows them to find the information they are looking for quickly and easily. Elements like headers, bold and highlighted text, bulleted lists, graphics, captions and more accomplish this. Enchanting Marketing offers the following (helpfully, bulleted) list of questions to evaluate whether your content is scannable to readers:
- Does your headline communicate what you’re about?
- Does your image caption communicate a message?
- Do your sub headlines summarize your key points?
- Do easy-to-scan bullet points reduce wordiness?
In general, “Your web visitor is hunting for information or products. Ensure he can understand your most important information by just glancing at your web page,” the same post says.
Concise Text
Because readers are looking to find information as quickly as possible, writing concise text is another key component of successful web writing. Users don’t stay on a page for very long. This is why marketers measure “bounce rate,” or the percentage of visitors who navigate away from content. To hold reader interest as well as maximize time on site, be as concise as possible. According to Buffer, the ideal length for a blog post is seven minutes, or 1,600 words. And for posts that incorporate many photos or other graphic elements, the average word count should be closer to 1,000. Though research varies from site to site, this gives content creators a good idea of what to aim for. Once again, Enchanting Marketing has provided a helpful checklist for keeping content short and sweet:
- Use short paragraphs
- Use short sentences
- Skip unnecessary words
- Avoid jargon
- Avoid the passive [voice]
- Avoid needless repetition
- Use the word “you”
Aside from actually writing less content, a good way to keep readers’ attention is to break up text into short paragraphs that can be easily scanned and digested. This works in tandem with concise text to ensure the user views as much content as possible.
Objective Language
Users want content to be easy to understand, and another way to accomplish this is by writing in a conversational, informal tone. Ensuring that your tone is objective makes information easier to process. Avoid overly promotional messaging because it makes users question the credibility of the content itself: “questioning the credibility of promotional statements seems to distract users from processing the meaning,” the Nielsen Norman Group says. This is also why Enchanting Marketing warns against using “clever phrasing.” Web writing should be as simple and easy to follow as possible. “Web visitors quickly glance at your web page before guessing whether they’re in the right place or not,” Enchanting Marketing says. “They just want to make a quick decision.”
Hypotext
One way to make your content more readable without sacrificing valuable information is to incorporate hypotext. According to Dejan Marketing, hypotext is “a way of revealing content on-demand. It acts like a traditional link, but it doesn’t interrupt user experience by sending readers to another page. Once clicked, the extra information is injected into a desired spot in the page. Another click hides it away.” By showing the most important parts of the content, readers can create their own experience. The same article provides several benefits of hypotext:
- Supports easy scanning and better content overview by removing visual clutter
- Encourages content consumption through low word count
- On-demand information retrieval enables interactivity and personalization
- Users stay on the page they’re reading, which minimizes interruption

From a content strategy perspective, hypotext also allows the writer to include more detailed information as an option while remaining concise.
As effective web writing becomes more and more important to overall marketing strategy, the volume of content being created is increasing at an unprecedented rate, according to Dejan Marketing. From blog posts to advertorials, opinion pieces and lists, the web is home to a wide variety of content competing for user attention. But if marketers can incorporate the best practices covered here, they stand to benefit from the world of opportunity that content marketing presents.
Creating optimized, high-quality content is one of the foundations of modern marketing strategy. If you are interested in topics like these that are relevant to the marketing industry, consider Concordia University, St. Paul’s online marketing degree program.